MPSC Civil Engineering Syllabus And Exam Pattern
MPSC सिव्हिल इंजिनीअरिंग अभ्यासक्रम 2023 प्रकाशित !!
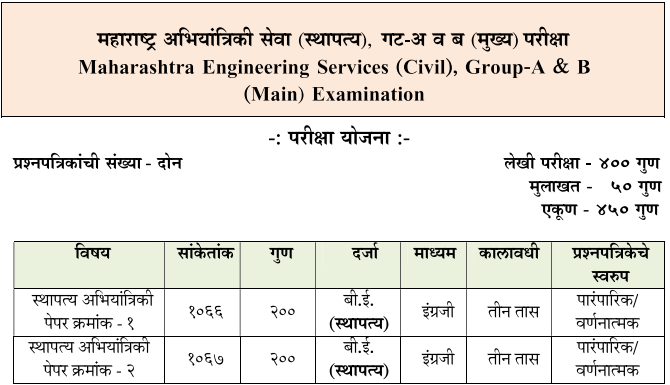
MPSC Civil Engineering Syllabus And Exam Pattern -The MPSC Civil Engineering Syllabus 2023 has been published by MPSC. MPSC Civil Engineering Syllabus is available for download on official website as well as here on this page. MPSC Civil Mains Exam consists of a Written Exam consisting of 400 Marks and an Interview 50 Marks. The main examination for the candidates will be held on Sunday, January 28, 2024 at Amravati, Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar, Nagpur, Nashik, Navi Mumbai and Pune District Students can download Whole MPSC Civil Engineering Syllabus from below link.
⏰MPSC Electrical Engineering Services Syllabus And Exam Pattern
⏰MPSC Civil Engineering Services Cut Off – स्थापत्य अभियांत्रिकी सेवा परीक्षा २०२१ कट ऑफ गुण
MPSC सिव्हिल इंजिनीअरिंग अभ्यासक्रम 2023 MPSC ने प्रकाशित केला आहे. एमपीएससी स्थापत्य अभियांत्रिकी अभ्यासक्रम अधिकृत वेबसाइटवर तसेच या पृष्ठावर डाउनलोड करण्यासाठी उपलब्ध आहे. MPSC नागरी मुख्य परीक्षेत 400 गुण आणि मुलाखत 50 गुणांची लेखी परीक्षा असते. स्टडनेट खालील लिंकवरून संपूर्ण MPSC सिव्हिल इंजिनिअरिंग अभ्यासक्रम डाउनलोड करू शकतात…!!
तसेच या संदर्भातील पुढील सर्व अपडेट्ससाठी या लिंक वरून आपण आमच्या टेलिग्राम चॅनलला जॉईन करावे किंवा या लिंक वरून महाभरती एक्सामची अधिकृत अँप आपल्या मोबाईल मध्ये डाउनलोड करावी आणि अधिक ताज्या आणि अधिकृत महाराष्ट्र परीक्षेच्या अपडेटसाठी MahaBharti.in/exam फॉलो करा:
⏰MPSC Mechanical Gr A And GR B Syllabus PDF
उमेदवारांची मुख्य परीक्षा रविवार, 28 जानेवारी 2024 रोजी अमरावती, छत्रपती संभाजी नगर, नागपूर, नाशिक, नवी मुंबई आणि पुणे जिल्हा येथे होणार आहे. !! Download Admit Card
MPSC Civil Engineering Services Exam Pattern 2023
How many marks are there in MPSC Civil Engineering mains exam?
MPSC Civil Engineering Syllabus And Exam Pattern – New Exam …
400 Marks
MPSC Civil Mains Exam consists of a Written Exam consisting of 400 Marks and an Interview 50 Marks.
MPSC Civil Engineering Syllabus 2023
MPSC Civil Engineering- Paper – I Syllabus
| Sr. No. | Topics |
| Section A | |
| 1 | Strength of materials
Stresses, strains, principal stresses, bending moments, shear forces and torsion theory, bending theory of beam, deflection of beam, theories of buckling of columns. |
| 2 | Theory of structures
Analysis of beams, frames and trusses, slope deflection method, moment distribution method. |
| 3 |
Computer aided analysis and design of structures Computer-aided analysis and design of structures, application of computer programming to structures. numerical methods such as: i. Finding area by Simpson’s rule, trapezoidal rule; ii. Finding root of an equation by a) Newton-Raphson techniques b) Bisection method iii. Solution of simultaneous equations by a) Gauss elimination method, b) Gauss Jordan method, c) Iteration method. |
| Section B | |
| 4 | Structural analysis
Analysis of arches and suspension cables, influence lines, stiffness and flexibility matrix methods. |
| 5 | Steel Structures
Plastic Analysis, Design of bolted and welded connections, columns, footings, trusses, steel beams, plate girders. |
| 6 | Construction Planning and management
Functions of management, Elements of material management, safety engineering, network analysis, construction equipment, site layout, quality control, agreement, PPP investment models, EPC, various acts related to workers and industry (workmen compensation act, factories act, minimum wages act, etc.) |
| Section C | |
| 7 | Design of Reinforced concrete Structures (WSM and Limit State)
Design of slab, beams, columns, footing. |
| 8 | Design of Reinforced concrete Structures (WSM and Limit State)
Retaining walls, tanks, building frames, staircases. |
| 9 | Bridge Engineering
Selection of site, types of bridges, discharge, waterway, spans, afflux, scour, standards, specifications, loads and forces, erection of superstructure, strengthening cofferdams, caissons. |
| Section D | |
| 10 | Concrete Technology
Properties of wet and hardened concrete, test on concrete, factors affecting concrete, water cement ratio, aggregate cement ratio, mix design, additives, design of form work, types of formwork. |
| 11 | Prestressed concrete
Principles of pre-stressing, materials used and their properties, permissible stresses as per I.S. codes, systems of pre-stressing, losses in pre-stress, design of pre-tensioned and post-tensioned beams- simply supported, rectangular and T- beams, cable profile, end block design, bridge girder. |
| 12 | Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical properties, stresses in soil, shear resistance, compaction, consolidation and earth pressure, stability of slopes, bearing capacity, settlements, shallow and deep foundations, basic engineering geology. |
MPSC Civil Engineering – Paper – II Syllabus
| Sr. No | Topics |
| Section A | |
| 1 | Surveying
Classification of surveys, measurement of distances-direct and indirect methods, optical and electronic devices, prismatic compass, local attraction; plane table surveying, levelling, volume calculation, contours, theodolite, theodolite traversing, omitted measurements, trigonometric levelling, tacheometry, curves, photogrammetry, geodetic surveying, hydrographic surveying, advanced instruments in surveying. |
| 2 | Engineering Materials
Properties of wet and hardened concrete, tests on concrete, factors affecting strength of concrete, water-cement ratio, aggregate-cement ratio, mix design, additives, design of form work, types of form work, bitumen, mastic asphalt, emulsion, cutback, stone matrix asphalt, fly ash, sustainable building materials, stones, bricks, cement, lime, mortar, timber, plastic, concrete, steel, paints and varnishes. |
| 3 | Building Planning and Construction
Principles of building planning and design, integrated approach, building byelaws, building services such as vertical transportation, water supply sanitation, thermal ventilation, lighting, acoustics, fire protection, electrical fittings. Types of foundations, stones, brick and block masonry, steel and reinforced cement concrete structures, floors, doors and windows, roofs, finishing works, water proofing. |
| Section B | |
| 4 | Fluid mechanics
Properties of fluids, fluid statics and buoyancy, kinematics and dynamics, flow measurement, flow in open channel, flow in closed conduits, dimensional and model analysis, losses in pipe flow, cavitations and separation, siphon, water hammer, boundary layer and control, pipe network. |
| 5 | Fluid machines
Hydraulic turbines, centrifugal pumps, reciprocating pumps, power house, classification and layout. |
| 6 | Irrigation Engineering
Water requirement of crops, methods of irrigation, lift irrigation, water logging, dams, spillways, energy dissipation, diversion head works, canal and canal structures, cross drainage works, river training works, lake tapping. |
Section C
Highway Engineering
Planning of highway systems, alignment and geometric design, horizontal and vertical curves, grade separation, cross sectional elements of highway, thin and ultra thin white topping, overlays, rigid and flexible pavement, traffic engineering.
Tunnel Engineering
Surveys, criteria for selection of size and shapes, driving in soft and hard grounds, mucking, dust control, ventilation, lighting and drainage, special methods of tunnelling, cut and cover method, TBM, NATM, tunnel lining, Irrigation and highway tunnelling, metro tunnelling.
Estimating, costing and valuation
Specification, estimation, costing, tenders and contracts, rate analysis, valuation, arbitration.
Section D
Engineering hydrology
Hydrological cycle, precipitation, evaporation, infiltration, runoff, hydrographs, reservoir planning & sediment control, floods, flood routing, ground water.
Environmental engineering
Water supply Engineering
Sources of supply, design of intakes, estimation of demand, water quality standards, primary and secondary treatment, maintenance of treatment units, conveyance and distribution of treated water, rural water supply.
Wastewater Engineering and Pollution Control
Quantity, collection and conveyance and quality, disposal, design of sewer and sewerage systems, pumping, characteristics of sewage and its treatment, rural sanitation, sources and effects of air and noise pollution, monitoring, standards.
Solid waste management
Sources, classification, collection and disposal.


Admit Card Out